AI智能体
什么是智能体
智能体是一个能够感知环境、进行推理、制定计划、做出决策并自主行动的AI系统,集成记忆、知识库和工具为一体。
- 感知环境:通过各种渠道理解用户的提问。
- 自主规划任务步骤:将复杂的任务分解成可执行的子任务。
- 主动调用工具:自主选择需要调用的工具。
- 进行多步推理:通过思维链逐步分析问题并推导解决方案。
- 持续学习和记忆过去的交互:保持上下文的连贯。
- 根据环境反馈调整行为:根据执行结果动态调整策略。
智能体分类
反应式智能体:根据输入和固定规则做出反应
有限规划智能体:能简单的多步执行,但是通常有预设和限制
自主规划智能体:能够根据任务目标自主分解任务、指定计划、选择工具一步一步进行调用,例如Open Manus
这类智能体能够通过思考-行动-观察的循环模式工作,直到完成目标。
智能体关键技术
CoT思维链
CoT(chain of thought)思维链是一种让AI像人类一样思考的技术,帮助AI将复杂的问题拆解思考,逐步完成。可以在输入Prompt时候,给模型额外的提示或者引导
例如如下提示词
You are an assistant focused on Chain of Thought reasoning. For each question, please follow these steps:
1. Break down the problem: Divide complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts
2. Think step by step: Think through each part in detail, showing your reasoning process
3. Synthesize conclusions: Integrate the thinking from each part into a complete solution
4. Provide an answer: Give a final concise answer
Your response should follow this format:
Thinking: [Detailed thought process, including problem decomposition, reasoning for each step, and analysis]
Answer: [Final answer based on the thought process, clear and concise]
Remember, the thinking process is more important than the final answer, as it demonstrates how you reached your conclusion.Agent Loop执行循环
在没有用户提问的情况下,自主重复执行推理和工具调用的过程,区别于传统的一问一答。
ReAct
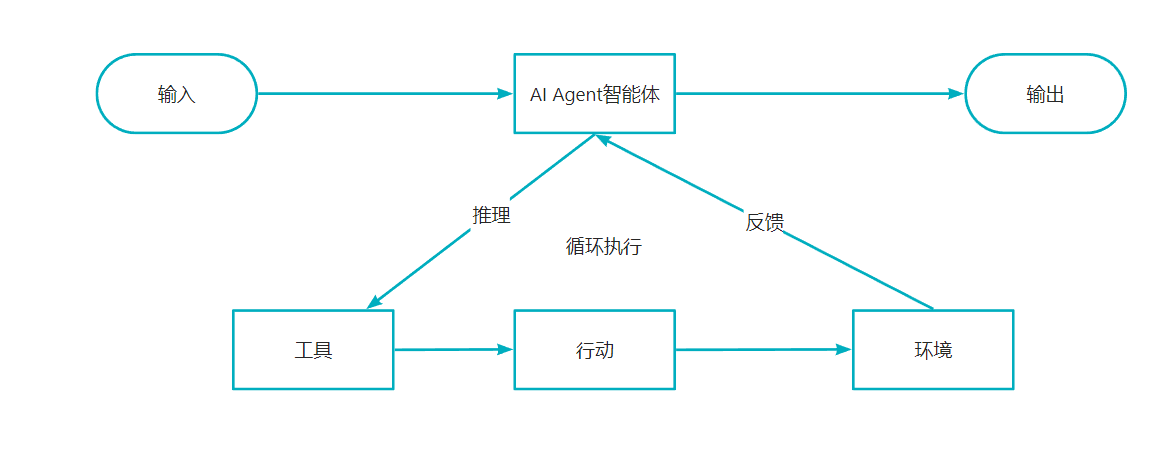
ReAct(Reasoning + Acting)结合推理和行动的智能体架构,模仿人类解决问题时,“思考-行动-观察”循环,目的是通过交互式决策决策解决复杂任务。
- 思考(Reason):将复杂任务拆分为多个步骤的任务,明确当前执行步骤
- 行动(Act):调用外部工具执行动作
- 观察(Observe):获取工具返回结果,反馈给智能体进行下一步决策
- 循环迭代:不对重复以上步骤,直到任务完成或者达到终止条件。
依赖环境
- AI模型
- 记忆系统
- 知识库
- 工具调用
Compute Use
允许智能体能够直接与计算机环境交互
OpenManus源码分析
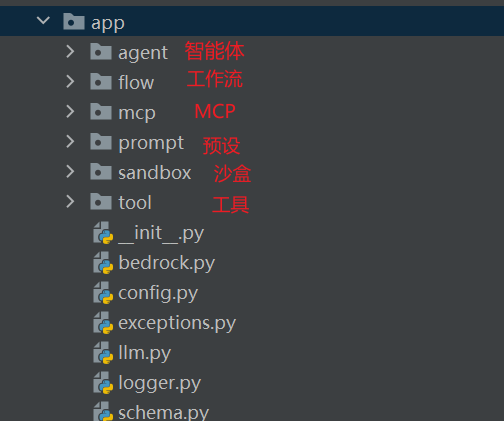
Agent
采用了分层的代理架构,不同的代理负责不同的功能,便于系统扩展。
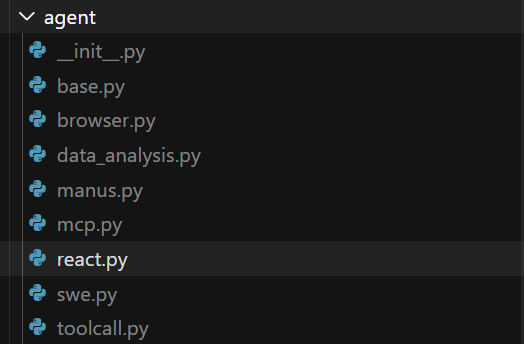
BaseAgent:最基础的代理抽象类,定义了所有代理的基本状态管理和执行循环
ReActAgent:实现 ReAct模式的代理,具有思考(Think)和行动(Act)两个主要步骤
ToolCallAgent:能够调用工具的代理,继承自ReActAgent并扩展了工具调用能力
Manus:具体实现的智能体实例,集成了所有能力并添加了更多专业工具
Tool目录
定义了各种的工具,例如网页搜索、文件操作等
Prompt
设置预设,可以参考相关预设。
自主实现Manus
BaseAgent基础类
/**
* 抽象基础类,用于管理代理状态和执行循环基础功能
*/
@Data
@Slf4j
public abstract class BaseAgent {
/**
* 代理名称
*/
private String name;
/**
* 系统预设
*/
private String systemPrompt;
private String nextStepPrompt;
/**
* 模型信息
*/
private ChatClient chatClient;
/**
* 存储AI聊天记录
*/
private List<Message> messageList = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 智能体运行状态
*/
private AgentState state = AgentState.IDLE;
/**
* 执行步数
*/
private Integer currentStep = 0;
private Integer maxSteps = 10;
public String run(String userPrompt) {
// 判断状态是否为空闲状态
if (this.state != AgentState.IDLE) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can not run agent in current state: " + this.state);
}
// 判断用户预设是否为空
if (StrUtil.isBlank(userPrompt)) {
throw new RuntimeException("User prompt can not be empty");
}
// 更新状态
this.state = AgentState.RUNNING;
// 记录消息上下文
messageList.add(new UserMessage(userPrompt));
// 保存消息
List<String> results = new ArrayList<>();
// 循环更新判断步数
try {
for (int i = 0; i < maxSteps && state != AgentState.FINISHED; i++) {
int stepNum = i + 1;
currentStep = stepNum;
log.info("[CurrentStep {} / MaxSteps{}] Running...", stepNum, maxSteps);
String result = step();
result = "Step " + stepNum + ":" + result;
results.add(result);
}
return StrUtil.join("\n", results);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error running agent", e);
} finally {
cleanup();
}
}
/**
* 执行单个步骤
*
* @return
*/
public abstract String step();
/**
* 清除资源
*/
protected void cleanup() {
}
}使用SSE实现文字流式输出
public SseEmitter runStream(String userPrompt) {
SseEmitter sseEmitter = new SseEmitter(300000L);
// 异步
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
// 判断状态是否为空闲状态
if (this.state != AgentState.IDLE) {
sseEmitter.send("Agent is not idle");
sseEmitter.complete();
}
// 判断用户预设是否为空
if (StrUtil.isBlank(userPrompt)) {
sseEmitter.send("User prompt can not be empty");
sseEmitter.complete();
}
// 更新状态
this.state = AgentState.RUNNING;
// 记录消息上下文
messageList.add(new UserMessage(userPrompt));
// 保存消息
List<String> results = new ArrayList<>();
// 循环更新判断步数
try {
for (int i = 0; i < maxSteps && state != AgentState.FINISHED; i++) {
int stepNum = i + 1;
currentStep = stepNum;
log.info("[CurrentStep {} / MaxSteps{}] Running...", stepNum, maxSteps);
String result = step();
result = "Step " + stepNum + ":" + result;
sseEmitter.send(result);
}
if (currentStep >= maxSteps) {
state = AgentState.FINISHED;
sseEmitter.send("Agent has finished running");
}
sseEmitter.complete();
} catch (Exception e) {
try {
state = AgentState.ERROR;
sseEmitter.send("Agent encountered an error: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception ex) {
sseEmitter.completeWithError(ex);
}
} finally {
cleanup();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
sseEmitter.completeWithError(e);
}
});
// 超时
sseEmitter.onTimeout(() -> {
this.state = AgentState.ERROR;
this.cleanup();
});
sseEmitter.onCompletion(() -> {
if (this.state == AgentState.RUNNING) {
this.state = AgentState.FINISHED;
}
this.cleanup();
});
return sseEmitter;
}ReActAgent思考-行动类
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true)
@Data
public abstract class ReActAgent extends BaseAgent {
/**
* 处理当前状态并且进行下一步行动
*
* @return true表示需要执行下一步行动,false表示不需要执行下一步行动
*/
public abstract boolean think();
/**
* 执行绝对的行动
*
* @return
*/
public abstract String act();
/**
* 执行单个步骤:思考和行动
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public String step() {
try {
// 判断是否需要执行
boolean shouldThink = think();
if (!shouldThink) {
return "Thinking complete - no action needed";
}
return act();
} catch (Exception e) {
return "Error Think or Act: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
}ToolCall工具调用类
基于Spring Al的工具调用能力,手动控制工具执行(推荐使用)。
Spring的ChatClient 已经支持选择工具进行调用(内部完成了think、act、observe)
基于Spring Al的工具调用能力,简化调用流程。
Spring Al 完全托管了工具调用,所有工具调用的代码作为think方法,而act方法不定义任何动作。
自主实现工具调用能力。
自己写Prompt,引导AI回复想要调用的工具列表和调用参数,然后再执行工具并将结果返送给 AI再次执行。
/**
* 处理工具调用的基础类
*/
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true)
@Data
@Slf4j
public class ToolCallAgent extends ReActAgent {
// 可调用的工具
private final ToolCallback[] toolCallbacks;
// 调用响应
private ChatResponse chatResponse;
// 工具调用管理者
private final ToolCallingManager toolCallingManager;
private ChatOptions chatOptions;
// 构造方法停止Spring AI内部的chat options
public ToolCallAgent(ToolCallback[] toolCallbacks) {
this.toolCallbacks = toolCallbacks;
this.toolCallingManager = ToolCallingManager.builder().build();
// 禁用系统内部Spring AI的思考和行动
this.chatOptions = DashScopeChatOptions.builder().withProxyToolCalls(true).build();
}
@Override
public boolean think() {
// 1. 判断预设是否为空
if (getNextStepPrompt() != null && getSystemPrompt() != null) {
UserMessage userMessage = new UserMessage(getNextStepPrompt());
// 添加消息
getMessageList().add(userMessage);
}
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(getMessageList(), chatOptions);
// 2.获取响应
try {
this.chatResponse = getChatClient()
.prompt(prompt)
.tools(toolCallbacks)
.system(getSystemPrompt())
.call().chatResponse();
// 3. 处理响应
AssistantMessage assistantMessage = this.chatResponse.getResult().getOutput();
String thinkResult = assistantMessage.getText();
List<AssistantMessage.ToolCall> toolCalls = assistantMessage.getToolCalls();
log.info(getName() + " 思考 " + thinkResult);
log.info(getName() + " 执行了" + toolCalls.size() + "个工具调用");
// 4. 汇总工具调用信息,重新写入消息
String toolCallInfo = toolCalls.stream()
.map(toolCall -> String.format("工具名称: %s,参数: %s", toolCall.name(), toolCall.arguments()))
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
log.info(getName() + " 工具调用信息: \n" + toolCallInfo);
if (toolCallInfo.isEmpty()) {
getMessageList().add(assistantMessage);
return false;
} else {
// 需要调用的时候无需记录助手消息,调用工具会自动记录
return true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(getName() + "助手思考出错" + e.getMessage());
getMessageList().add(new AssistantMessage(getName() + "助手思考出错" + e.getMessage()));
return false;
}
}
@Override
public String act() {
// 判断是否有工具调用
if (!chatResponse.hasToolCalls()) {
return "no-tool-calls";
}
// 工具调用,设置消息
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(getMessageList(), chatOptions);
ToolExecutionResult toolExecutionResult = toolCallingManager.executeToolCalls(prompt, chatResponse);
setMessageList(toolExecutionResult.conversationHistory());
// 返回工具调用结果,取最后一条消息
ToolResponseMessage responseMessage = (ToolResponseMessage) CollUtil.getLast(toolExecutionResult.conversationHistory());
String res = responseMessage.getResponses().stream().map(response -> "工具" + response.name() + "调用结果:" + response.responseData())
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
log.info(res);
// 如果结束就终止运行
boolean terminateToolCalled = responseMessage.getResponses().stream().anyMatch(response -> "doTerminate".equals(response.name()));
if (terminateToolCalled) {
setState(AgentState.FINISHED);
}
log.info("do terminate toll" + terminateToolCalled);
return res;
}
}工具注册
@Configuration
public class ToolRegistration {
@Value("${search.api-key}")
private String apiKey;
@Bean
public ToolCallback[] allTools() {
FileOperationTool fileOperationTool = new FileOperationTool();
PDFGenerateTool pdfGenerateTool = new PDFGenerateTool();
ResourceDownloadTool resourceDownloadTool = new ResourceDownloadTool();
TerminalOperationTool terminalOperationTool = new TerminalOperationTool();
WebOperationTool webOperationTool = new WebOperationTool(apiKey);
WebScrapingTool webScrapingTool = new WebScrapingTool();
CurrentDateTool currentDateTool = new CurrentDateTool();
TerminateTool terminateTool = new TerminateTool();
MarkdownGenerateTool markdownGenerateTool =new MarkdownGenerateTool();
return ToolCallbacks.from(
fileOperationTool,
pdfGenerateTool,
resourceDownloadTool,
terminalOperationTool,
webOperationTool,
webScrapingTool,
currentDateTool,
terminateTool,
markdownGenerateTool
);
}
}AI智能体
其他方法可以调用这个,设置智能体的各种参数
@Component
public class FlyManus extends ToolCallAgent {
public FlyManus(ToolCallback[] allTools, ChatModel dashscopeChatModel) {
super(allTools);
this.setName("flyManus");
String SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
You are FlyManus, an all-capable AI assistant, aimed at solving any task presented by the user.
You have various tools at your disposal that you can call upon to efficiently complete complex requests.
""";
this.setSystemPrompt(SYSTEM_PROMPT);
String NEXT_STEP_PROMPT = """
Based on user needs, proactively select the most appropriate tool or combination of tools.
For complex tasks, you can break down the problem and use different tools step by step to solve it.
After using each tool, clearly explain the execution results and suggest the next steps.
If you want to stop the interaction at any point, use the `terminate` tool/function call.
""";
this.setNextStepPrompt(NEXT_STEP_PROMPT);
this.setMaxSteps(20);
// 初始化客户端
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(dashscopeChatModel)
.defaultAdvisors(new MyAdvisors())
.build();
this.setChatClient(chatClient);
}
}运行结果
@Resource
private FlyManus flyManus;
@Test
public void testManus() {
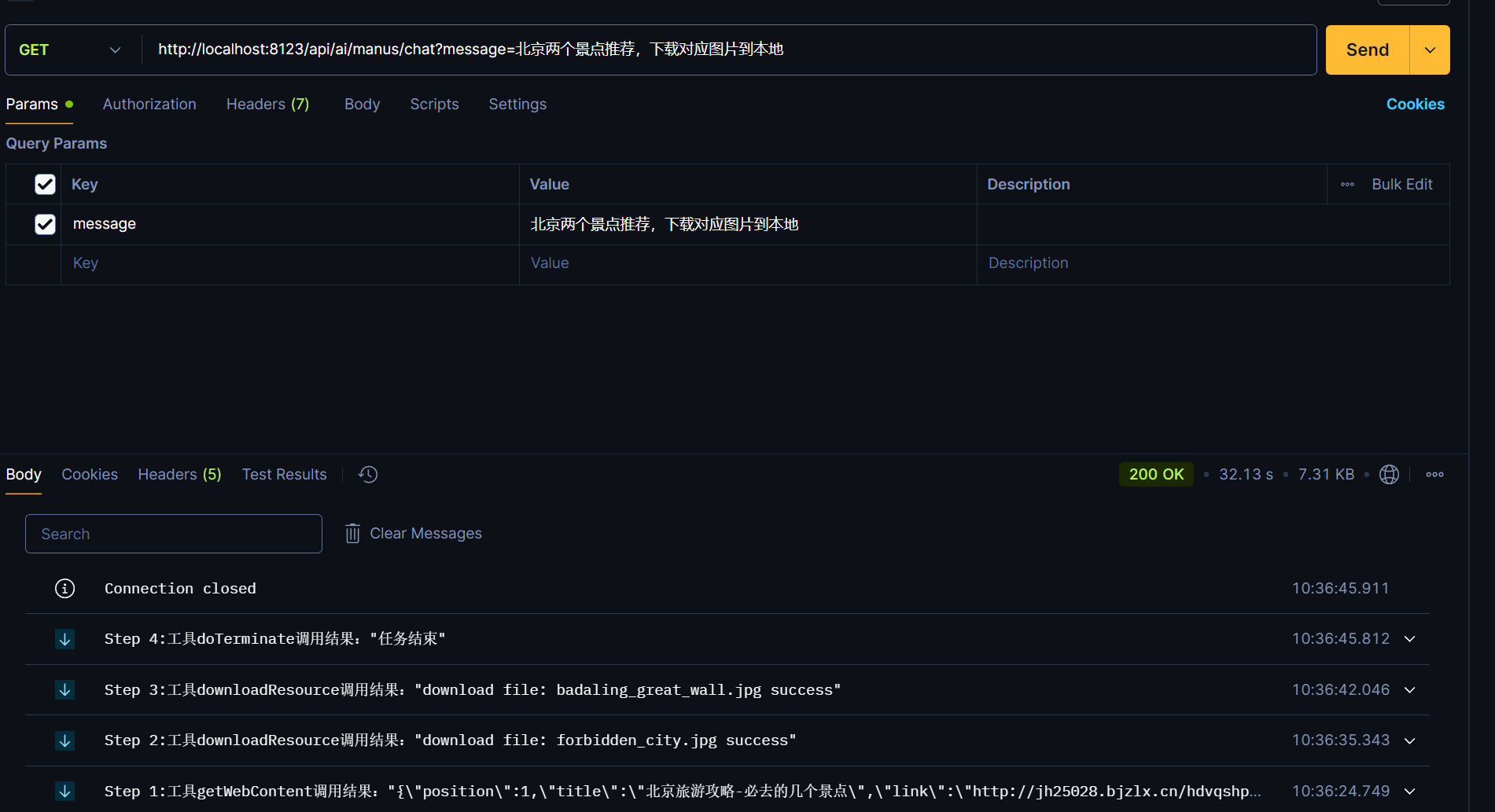
String prompt = "请给我推荐5个北京的景点,并且搜索对应的图片,请按照标题:景点名称,正文:图片,景点介绍这种格式,以中文Markdown格式输出";
String res = flyManus.run(prompt);
System.out.println(res);
}
我们可以看到详细的工具调用信息,执行步骤。
流式输出
@Resource
private ToolCallback[] allTools;
@Resource
private ChatModel dashscopeChatModel;
@GetMapping("/manus/chat")
public SseEmitter doChatWithManus(String message) {
FlyManus flyManus = new FlyManus(allTools, dashscopeChatModel);
return flyManus.runStream(message);
}
智能体工作流
单一的工作流无法满足不同的场景需求,我们可以采用智能体工作流,允许多个智能体同时协同工作。
- Prompt Calling提示链工作流
将复杂任务拆解成一个一个子任务,每个任务由前一个输出推进执行。
- Routing路由分流工作流
系统根据用户输入的类型和内容,分发给适合的智能体执行
- Parallelization并行化工作流
任务会被拆分成多个子任务,智能体并行执行子任务,最后将结果整合,得出最终结果
- Orchestrator-Workers 协调器-执行者工作流
引入一个管理者,会根据任务拆解出多个子任务,分发给多个智能体,最后再整合结果。适合任务结构不确定、需要动态分解的复杂场景。
- Evaluator-Optimzer 评估-优化循环工作流
模拟人类的 ”写-评-改“过程,一个智能体负责初步结果,另一个智能体负责评估和反馈。
OWL框架
**OWL (Optimized Workforce Learning)**是由CAMEL-AI团队开源的一款面向多智能体协作与真实世界任务自动化的前沿 框架。通过OWL,AI智能体可以执行终端命令、访问网络资、运行各种编程语言的代码、使用各种开发工具等等。
多智能体协作:OWL支持多个智能体之间的动态交互与协作,能够模拟真实团队协作场景,适合解决需要多角色、多技能配合的复杂任务。
丰富的工具集成:内置了浏览器自动化、代码执行、文档处理、音视频分析、搜索引擎等多种工具包,支持多模态任务(如网页操作、图片/视频/音频分析等)。
MCP协议支持:通过MCP,OWL能够与外部工具和数据源标准化对接,极大扩展了智能体的能力边界。
可定制与易用性:用户可以根据实际需求灵活配置和组合所需工具,优化性能和资源消耗。
Web 可视化界面:提供基于Gradio的本地Web Ul,支持模型选择、环境变量管理、交互历史查看等功能,方便开 发和调试。
A2A协议
A2A协议主要目的是让智能体之间能够直接交流与协作,相当于智能体直接通信的协议。
贡献者
flycodeu
版权所有
版权归属:flycodeu
