SpringAI Tools
Tool Calling
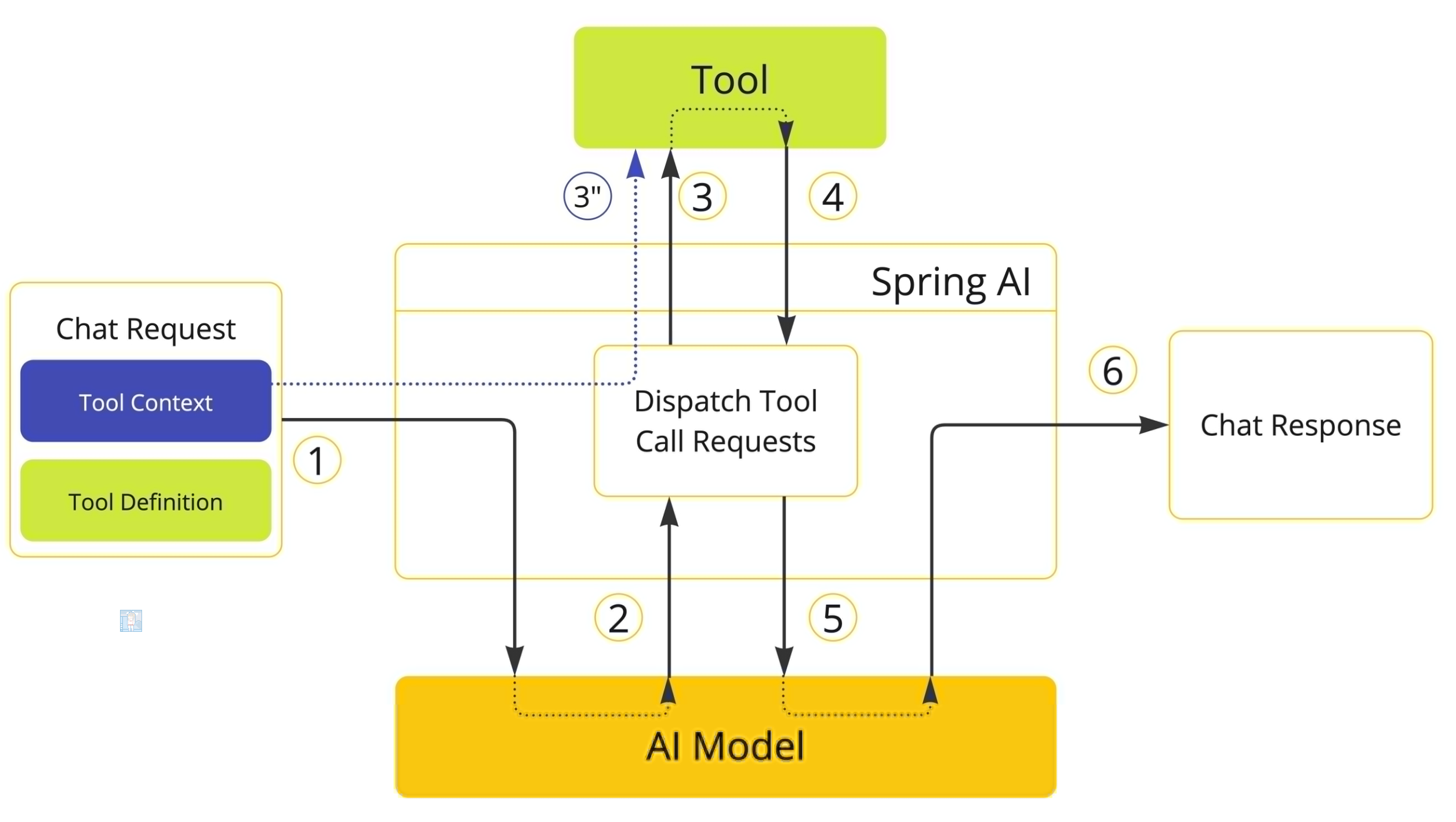
执行流程
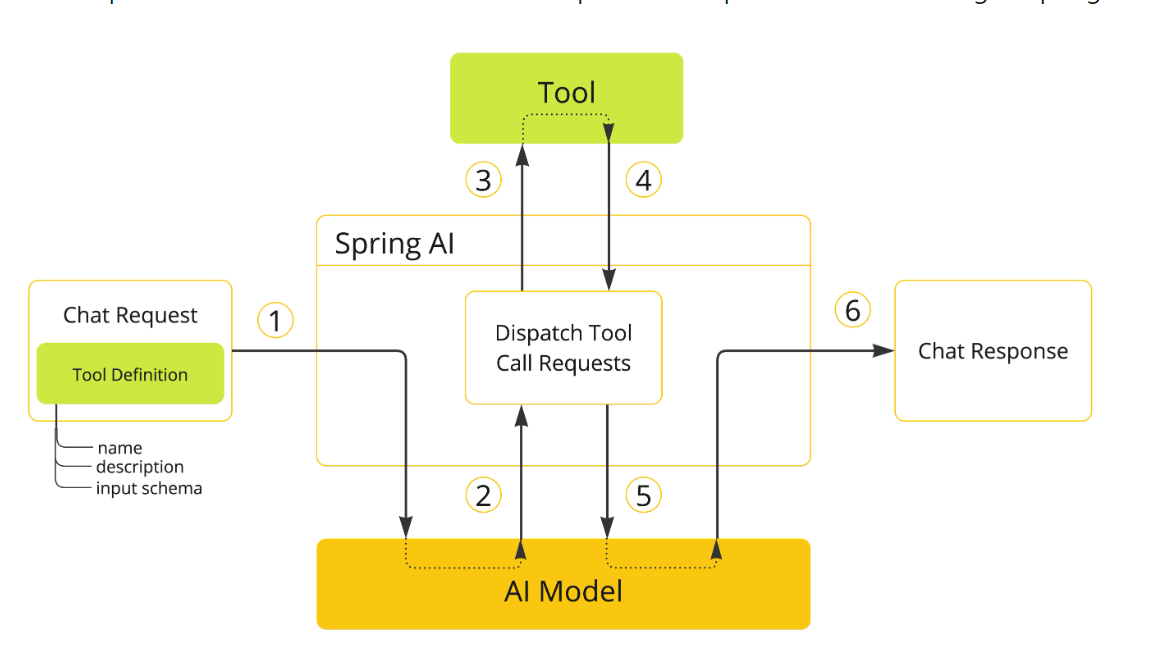
Methods模式:使用@Tools以及@ToolParam绑定工具
public class WeatherTools {
@Tool(description = "Get current weather by city name")
public String getWeather(@ToolParam(description = "The city name") String cityName) {
return "Current weather in " + cityName + ": sunny,30℃";
}
}
// 调用方式
ChatClient.create(chatModel).prompt("获取北京的天气信息").tools(new WeatherTools()).call();Functions模式:使用@Bean注解
@Configuration
public class ToolConfig {
@Bean
@Description("Get current weather for a location")
public Function<WeatherRequest, WeatherResponse> weatherFunction() {
return request -> new WeatherResponse("Weather in " + request.getCity() + ": Sunny, 25°C");
}
}
// 使用方式
ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What's the weather in Beijing?")
.functions("weatherFunction")
.call();定义工具
注解式
使用@Tools
public class WeatherTools {
@Tool(description = "Get current weather by city name")
public String getWeather(@ToolParam(description = "The city name") String cityName) {
return "Current weather in " + cityName + ": sunny,30℃";
}
}编程式
首先需要定义好工具类
class WeatherTools {
@Tool(description = "获取指定城市的当前天气情况")
String getWeather(@ToolParam(description = "城市名称") String city) {
return "北京今天晴朗,气温30°C";
}
}将工具类转换为ToolCallBack工具定义类
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(WeatherTools.class, "getWeather", String.class);
ToolCallback toolCallback = MethodToolCallback.builder()
.toolDefinition(ToolDefinition.builder(method)
.description("获取指定城市的当前天气情况")
.build())
.toolMethod(method)
.toolObject(new WeatherTools())
.build();使用工具
- 按需使用
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("北京今天天气怎么样?")
.tools(new WeatherTools()) // 在这次对话中提供天气工具
.call()
.content();- 全局使用
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultTools(new WeatherTools(), new TimeTools()) // 注册默认工具
.build();- 底层调用,绑定ChatModel
// 先得到工具对象
ToolCallback[] weatherTools = ToolCallbacks.from(new WeatherTools());
// 绑定工具到对话
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(weatherTools)
.build();
// 构造 Prompt 时指定对话选项
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("北京今天天气怎么样?", chatOptions);
chatModel.call(prompt);- 动态解析
ToolCallbackResolver使用适合工具需要根据上下文动态确定的场景
工具生态
Spring AI Alibaba但是里面只提供了一个,可以再官方代码仓库查看其它工具官方仓库地址
工具开发
文件操作
/**
* 文件读写工具类
*/
public class FileOperationTool {
private final String FILE_DIR = FileConstant.tempDir + "/file";
@Tool(description = "Read content from a file")
public String readFile(@ToolParam(description = "Name of the file to read") String fileName) {
String filePath = FILE_DIR + "/" + fileName;
try {
return FileUtil.readUtf8String(filePath);
} catch (Exception e) {
return "Error reading file: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
@Tool(description = "Write content to a file")
public String writeFile(@ToolParam(description = "Name of the file to write") String fileName, @ToolParam(description = "the content to write to the file") String content) {
String filePath = FILE_DIR + "/" + fileName;
try {
FileUtil.mkdir(FILE_DIR);
FileUtil.writeUtf8String(content, filePath);
return "File written successfully: " + filePath;
} catch (Exception e) {
return "Error writing file: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
}测试
@SpringBootTest
@ActiveProfiles("local")
public class ToolsTest {
@Test
public void writeFile() {
FileOperationTool tool = new FileOperationTool();
String fileName = "智能体AI.txt";
String content = " 我是测试文件内容";
String res = tool.writeFile(fileName, content);
System.out.println(res);
}
@Test
public void readFile(){
FileOperationTool tool = new FileOperationTool();
String fileName = "智能体AI.txt";
String s = tool.readFile(fileName);
System.out.println(s);
}
}联网搜索
可以使用Search API等专业网页搜索API实现多个网站获取内容,也可以通过爬虫等方式爬取搜索引擎等相关信息。
/**
* 联网搜索
*/
public class WebOperationTool {
public static final String WEB_URL = "https://www.searchapi.io/api/v1/search";
private final String apiKey;
public WebOperationTool(String apiKey) {
this.apiKey = apiKey;
}
@Tool(description = "Search for information from Baidu Search Engine")
public String getWebContent(@ToolParam(description = "Search key word") String query) {
// 1. 构造请求参数
Map<String, Object> param = new HashMap<>();
param.put("engine", "baidu");
param.put("q", query);
param.put("api_key", apiKey);
// 2. 发送请求
try {
String response = HttpUtil.get(WEB_URL, param);
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONUtil.parseObj(response);
JSONArray organicResults = jsonObject.getJSONArray("organic_results");
// 前5条
List<Object> objects = organicResults.subList(0, 5);
String result = objects.stream().map(obj -> {
JSONObject jsonObject1 = (JSONObject) obj;
return jsonObject1.toString();
}).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
return "Error search baidu: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
}测试调用
@Value("${search.api-key}")
private String apikey;
@Test
public void searchOnLine() {
WebOperationTool tool = new WebOperationTool(apikey);
String content = tool.getWebContent("大熊猫");
System.out.println(content);
}
后续只需要过滤出符合我们需求的数据即可。
网页抓取
可以使用jsoup抓取网页。
- 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jsoup</groupId>
<artifactId>jsoup</artifactId>
<version>1.19.1</version>
</dependency>- 简单获取网页html内容
/**
* 网页抓取工具类
*/
public class WebScrapingTool {
@Tool(description = "Scrape the content of a web page")
public String scrapeWebPage(@ToolParam(description = "url of the web to scrape") String url) {
try {
Document document = Jsoup.connect(url).get();
return document.html();
} catch (Exception e) {
return "Error scrape web: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
}目前只会返回对应的网页html信息,可以获取更加详细信息,详情可以参考在线抓取图片
- 测试
@Test
public void searchOnLine() {
WebOperationTool tool = new WebOperationTool(apikey);
String content = tool.getWebContent("大熊猫");
System.out.println(content);
}
终端操作
可以使用ProcessBuilder,在windows和linux不同环境,需要使用不同的Process方式。
public class TerminalOperationTool {
@Tool(description = "Execute a terminal command and return the output")
public String executeTerminalCommand(@ToolParam(description = "Execute command") String command) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
try {
ProcessBuilder builder = new ProcessBuilder("cmd.exe", "/c", command);
// Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
Process process = builder.start();
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream(),"GBK"))) {
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuilder.append(line).append("\n");
}
int exitCode = process.waitFor();
if (exitCode != 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("Terminal command failed with exit code " + exitCode);
}
process.destroy();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
return "Error executing terminal command: " + e.getMessage();
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
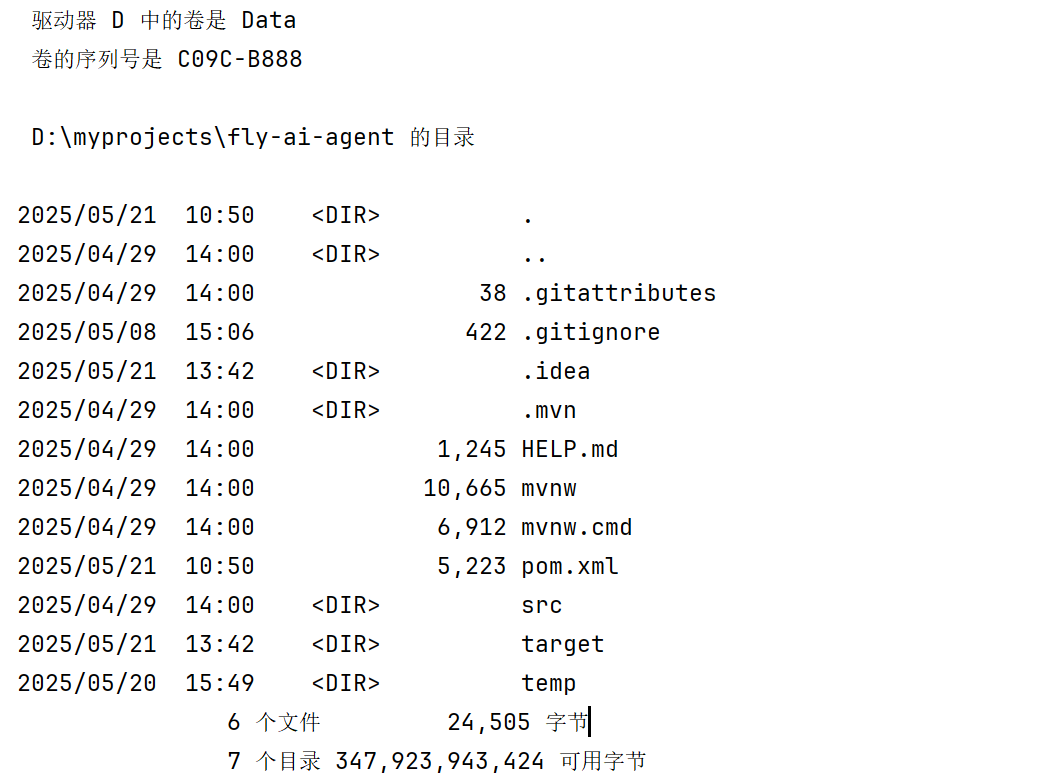
} @Test
public void executeTerminalCommand() {
String command = "dir";
TerminalOperationTool tool = new TerminalOperationTool();
String res = tool.executeTerminalCommand(command);
System.out.println(res);
}
资源下载
通过指定URL下载文件到本地
public class ResourceDownloadTool {
@Tool(description = "Download file from url")
public String downloadResource(
@ToolParam(description = "URL of the resource to download")
String url,
@ToolParam(description = "Name of the file to save the download resource")
String fileName) {
// 设置下载地址
String fileDir = FileConstant.tempDir + "/download";
String filePath = fileDir + "/" + fileName;
// 下载文件
try {
File dir = FileUtil.mkdir(fileDir);
HttpUtil.downloadFile(url, filePath);
return "download file: " + fileName + " success";
} catch (Exception e) {
return "Error download file " + e.getMessage();
}
}
}@Test
public void download() {
String url = "https://www.codefather.cn/logo.png";
String fileName = "logo.png";
ResourceDownloadTool tool = new ResourceDownloadTool();
String res = tool.downloadResource(url, fileName);
System.out.println(res);
}PDF生成
可以使用itext-java这个工具生成PDF文件
引入依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.itextpdf/itext-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.itextpdf</groupId>
<artifactId>itext-core</artifactId>
<version>9.1.0</version>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.itextpdf/font-asian -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.itextpdf</groupId>
<artifactId>font-asian</artifactId>
<version>9.1.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>生成PDF工具类
public class PDFGenerateTool {
@Tool(description = "Generate a PDF with given content")
public String generatePDF(
@ToolParam(description = "Name of the file to save the generated PDF")
String fileName,
@ToolParam(description = "Content to be written in the PDF")
String content) {
// 设置下载地址
String fileDir = FileConstant.tempDir + "/pdf";
String filePath = fileDir + "/" + fileName ;
try {
FileUtil.mkdir(fileDir);
try (PdfWriter pdfWriter = new PdfWriter(filePath);
PdfDocument pdfDocument = new PdfDocument(pdfWriter);
Document document = new Document(pdfDocument)) {
// 使用内置中文
PdfFont pdfFont = PdfFontFactory.createFont("STSong-Light", "UniGB-UCS2-H");
document.setFont(pdfFont);
// 创建段落
Paragraph paragraph = new Paragraph(content);
document.add(paragraph);
}
return "PDF Generated Successfully to " + filePath;
} catch (Exception e) {
return "Error PDF Generated file: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
}集中注册
@Configuration
public class ToolRegistration {
@Value("${search.api-key}")
private String apiKey;
@Bean
public ToolCallback[] allTools() {
FileOperationTool fileOperationTool = new FileOperationTool();
PDFGenerateTool pdfGenerateTool = new PDFGenerateTool();
ResourceDownloadTool resourceDownloadTool = new ResourceDownloadTool();
TerminalOperationTool terminalOperationTool = new TerminalOperationTool();
WebOperationTool webOperationTool = new WebOperationTool(apiKey);
WebScrapingTool webScrapingTool = new WebScrapingTool();
return ToolCallbacks.from(
fileOperationTool,
pdfGenerateTool,
resourceDownloadTool,
terminalOperationTool,
webOperationTool,
webScrapingTool
);
}
}- 工厂模式:allTools()方法作为一个工厂方法,负责创建和配置多个工具实例,然后将它们包装成统一的数组返回。这符合工厂模式的核心思想-集中创建对象并隐藏创建细节。
- 依赖注入模式:通过 @value 注解注入配置值,以及将创建好的工具通过Spring容器注入到需要它们的组件中。
- 注册模式:该类作为一个中央注册点,集中管理和注册所有可用的工具,使它们能够被系统其他部分统一访问。
- 适配器模式的应用:ToolCallbacks.from 方法可以看作是一种适配器,它将各种不同的工具类转换为统一的ToolCallback数组,使系统能够以一致的方式处理它们。
测试集中注册
@Resource
private ToolCallback[] allTools;
private final ChatClient chatClient;
@Resource
private VectorStore loveAppVectorStore;
public LoveApp(ChatModel dashscopeChatModel, VectorStore loveAppVectorStore) {
this.loveAppVectorStore = loveAppVectorStore;
// 初始化基于内存的对话记忆
ChatMemory chatMemory = new LocalMemory(baseDir);
//SystemPromptTemplate systemPromptTemplate = new SystemPromptTemplate(systemResource.toString());
chatClient = ChatClient.builder(dashscopeChatModel)
.defaultSystem(SYSTEM_PROMPT)
.defaultAdvisors(
new MessageChatMemoryAdvisor(chatMemory),
new WordAdvisors()
)
.build();
}
public String doChatWithTools(String message, String chatId) {
ChatResponse chatResponse = chatClient
.prompt()
.user(message)
.system(SYSTEM_PROMPT)
.advisors(spec -> spec.param(CHAT_MEMORY_CONVERSATION_ID_KEY, chatId)
.param(CHAT_MEMORY_RETRIEVE_SIZE_KEY, 10))
.tools(allTools)
.call()
.chatResponse();
String content = chatResponse.getResult().getOutput().getText();
log.info(content);
return content;
} @Test
void doChatWithTools() {
String chatId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
String message = "给我生成北京的旅游景点PDF,包含时间、计划和费用,生成10条信息";
loveApp.doChatWithTools(message, chatId);
}
底层原理
ToolCallback
ToolCallback继承于FunctionCallback,实现如下接口
public interface ToolCallback {
/**
* Definition used by the AI model to determine when and how to call the tool.
*/
ToolDefinition getToolDefinition();
/**
* Metadata providing additional information on how to handle the tool.
*/
ToolMetadata getToolMetadata();
/**
* Execute tool with the given input and return the result to send back to the AI model.
*/
String call(String toolInput);
/**
* Execute tool with the given input and context, and return the result to send back to the AI model.
*/
String call(String toolInput, ToolContext tooContext);
}ToolDefinition接口为 AI 模型提供了解工具可用性所需的信息,包括工具名称、描述和输入架构。getToolMetadata返回该工具的元数据- 两个call()是工具的执行入口,分别支持有上下文和无上下文的调用场景
ToolDefinition
public interface ToolDefinition {
String name();
String description();
String inputSchema();
static DefaultToolDefinition.Builder builder() {
return DefaultToolDefinition.builder();
}
static DefaultToolDefinition.Builder builder(Method method) {
Assert.notNull(method, "method cannot be null");
return DefaultToolDefinition.builder().name(ToolUtils.getToolName(method)).description(ToolUtils.getToolDescription(method)).inputSchema(JsonSchemaGenerator.generateForMethodInput(method, new JsonSchemaGenerator.SchemaOption[0]));
}
static ToolDefinition from(Method method) {
return builder(method).build();
}
}
- JsonSchemaGenerator 会解析方法签名和注解,自动生成符合JSON Schema规范的参数定义,作为ToolDefinition的 一部分提供给AI大模型
- ToolCallResultConverter 负责将各种类型的方法返回值统一转换为字符串,便于传递给AI大模型处理
- MethodToolCallback 实现了对注解方法的封装,使其符合接口规范
我们只需要专注一业务逻辑,而不需要关心底层通信和参数转换的复杂细节,我们也可以通过自定义ToolCallResultConverter实现
Tool Context 工具上下文
Spring AI 支持通过 ToolContext API 将额外的上下文信息传递给工具。此功能允许您提供额外的用户提供的数据,这些数据可与 AI 模型传递的工具参数一起在工具执行中使用。
class CustomerTools {
@Tool(description = "Retrieve customer information")
Customer getCustomerInfo(Long id, ToolContext toolContext) {
return customerRepository.findById(id, toolContext.get("tenantId"));
}
}ToolContext 使用用户在调用 ChatClient 时提供的数据进行填充
ChatModel chatModel = ...
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("Tell me more about the customer with ID 42")
.tools(new CustomerTools())
.toolContext(Map.of("tenantId", "acme"))
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(response);也可以直接调用ChatModel定义工具上下文
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback[] customerTools = ToolCallbacks.from(new CustomerTools());
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(customerTools)
.toolContext(Map.of("tenantId", "acme"))
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("Tell me more about the customer with ID 42", chatOptions);
chatModel.call(prompt);本质上ToolContext是一个Map
public class ToolContext {
private final Map<String, Object> context;
}这些信息不会传递给AI模型,只有在程序内部使用,适用于:
- 用户认证信息:可以在上下文传递用户token,而不暴露给模型
- 请求追踪:上下文加入ID,便于日志追踪和调试
- 自定义配置:不同场景传递不同信息
Return Direct 直接返回
- 定义工具时,将 returnDirect 属性设为true
- 当模型请求调用这个工具时,应用程序执行工具并获取结果
- 结果直接返回给调用者,不再发送回模型进行进一步处理
这种模式很适合需要返回二进制数据(比如图片/文件)的工具、返回大量数据而不需要AI解释的工具,以及产生明确 结果的操作(如数据库操作)。
Tool Execution 工具执行
ToolCallingManager是管理AI工具调用全流程的核心组件,负责将AI模型的响应执行对应的工具并返回结果给大模型。
public interface ToolCallingManager {
/**
* Resolve the tool definitions from the model's tool calling options.
* 模型工具调用选项中解析工具定义
*/
List<ToolDefinition> resolveToolDefinitions(ToolCallingChatOptions chatOptions);
/**
* Execute the tool calls requested by the model.
* 执行模型对应的工具调用
*/
ToolExecutionResult executeToolCalls(Prompt prompt, ChatResponse chatResponse);
/**
* Create a default {@link ToolCallingManager} builder.
*/
static DefaultToolCallingManager.Builder builder() {
return DefaultToolCallingManager.builder();
}
} public ToolExecutionResult executeToolCalls(Prompt prompt, ChatResponse chatResponse) {
Assert.notNull(prompt, "prompt cannot be null");
Assert.notNull(chatResponse, "chatResponse cannot be null");
Optional<Generation> toolCallGeneration = chatResponse.getResults()
.stream()
.filter(g -> !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(g.getOutput().getToolCalls()))
.findFirst();
if (toolCallGeneration.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No tool call requested by the chat model");
}
AssistantMessage assistantMessage = toolCallGeneration.get().getOutput();
ToolContext toolContext = buildToolContext(prompt, assistantMessage);
InternalToolExecutionResult internalToolExecutionResult = executeToolCall(prompt, assistantMessage,
toolContext);
List<Message> conversationHistory = buildConversationHistoryAfterToolExecution(prompt.getInstructions(),
assistantMessage, internalToolExecutionResult.toolResponseMessage());
return ToolExecutionResult.builder()
.conversationHistory(conversationHistory)
.returnDirect(internalToolExecutionResult.returnDirect())
.build();
}基本流程就是从历史上下文中拿出关键信息,判断是否有工具需要调用,有工具调用,执行完成获取结果,然后拼接到上下文。
框架控制的工具执行
- 框架自动检测模型是否请求调用工具
- 自动执行工具调用并获取结果
- 自动将结果发送回模型
- 管理整个对话流程直到得到最终答案
用户控制的工具执行
对于需要更精细控制复杂场景,可以通过设置ToolCallingChatOptions禁止内部工具执行,然后可以自定义执行工具流程。
// 配置不自动执行工具
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(ToolCallbacks.from(new WeatherTools()))
.internalToolExecutionEnabled(false) // 禁用内部工具执行
.build();// 创建工具调用管理器
ToolCallingManager toolCallingManager = DefaultToolCallingManager.builder().build();
// 创建初始提示
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("xxxx", chatOptions);
// 发送请求给模型
ChatResponse chatResponse = chatModel.call(prompt);
// 手动处理工具调用循环
while (chatResponse.hasToolCalls()) {
// 执行工具调用
ToolExecutionResult toolExecutionResult = toolCallingManager.executeToolCalls(prompt, chatResponse);
// 创建包含工具结果的新提示
prompt = new Prompt(toolExecutionResult.conversationHistory(), chatOptions);
// 再次发送请求给模型
chatResponse = chatModel.call(prompt);
}
// 获取最终回答
System.out.println(chatResponse.getResult().getOutput().getText());异常处理
里面内置了一个异常处理ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor {
/**
* 将工具抛出的异常转换为发送给 AI 模型的字符串,或者抛出一个新异常由调用者处理
*/
String process(ToolExecutionException exception);
}默认实现类提供两种处理策略
- alwaysThrow 参数为false:将异常信息作为错误消息返回给AI模型,允许模型根据错误信息调整策略
- alwaysThrow 参数为true:直接抛出异常,中断当前对话流程,由应用程序处理
也可以实现自定义异常处理
@Bean
ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor customExceptionProcessor() {
return exception -> {
if (exception.getCause() instanceof IOException) {
// 网络错误返回友好消息给模型
return "Unable to access external resource. Please try a different approach.";
} else if (exception.getCause() instanceof SecurityException) {
// 安全异常直接抛出
throw exception;
}
// 其他异常返回详细信息
return "Error executing tool: " + exception.getMessage();
};
}工具解析
除了使用ToolCallBack交给AI执行工具,也可以通过名称动态解析工具,通过ToolCallbackResolver接口实现的
public interface ToolCallbackResolver {
/**
* 根据给定的工具名称解析对应的ToolCallback
*/
@Nullable
ToolCallback resolve(String toolName);
}// 客户端只需提供工具名称
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What's the weather in Beijing?")
.toolNames("weatherTool", "timeTool") // 只提供名称
.call()
.content();也可以自定义解析逻辑
@Bean
ToolCallbackResolver customToolCallbackResolver() {
Map<String, ToolCallback> toolMap = new HashMap<>();
toolMap.put("weatherTool", new WeatherToolCallback());
toolMap.put("timeTool", new TimeToolCallback());
return toolName -> toolMap.get(toolName);
}也可以扩展当前的解析器
@Bean
ToolCallbackResolver customToolCallbackResolver() {
Map<String, ToolCallback> toolMap = new HashMap<>();
toolMap.put("weatherTool", new WeatherToolCallback());
toolMap.put("timeTool", new TimeToolCallback());
return toolName -> toolMap.get(toolName);
}贡献者
flycodeu
版权所有
版权归属:flycodeu
